Problems of Asphalt Roadways – 16 Challenges Underfoot
The resilience of asphalt roadways is often overshadowed by inherent problems, presenting significant challenges to their longevity and safety.
Asphalt roadways face numerous problems that significantly affect their integrity and functionality, including:
- Alligator cracking
- Potholes
- Rutting
- Fatigue cracking
- Upheaval
- Reflection cracking
- Edge cracking
- Cracking
- Depressions
- Patch failures
- Shoving
- Corrugation and shoving
- Raveling
- Bleeding
- Polished aggregate
- Oil
These issues can compromise road safety, necessitate frequent repairs, and increase maintenance costs, highlighting the need for durable paving solutions and regular upkeep.
Dive deeper into the causes, prevention strategies, and innovative solutions for addressing these asphalt roadway challenges, ensuring safer and more resilient infrastructure.
1. Alligator cracking
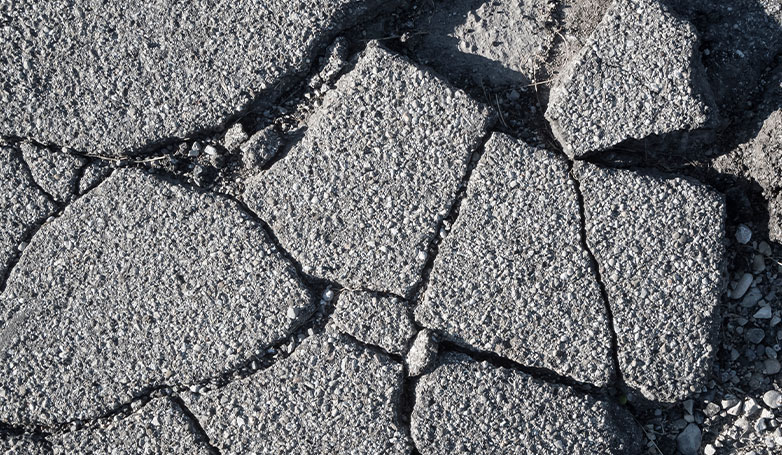

Alligator cracking is a type of pavement distress that signifies structural failure of the asphalt surface, often due to a weakened base or subgrade, inadequate pavement thickness, and poor drainage. It appears as interconnected cracks resembling alligator skin, primarily caused by the fatigue of the asphalt layer under repeated loading.
How to Solve
The effective repair method involves removing the affected area and reconstructing the failed sections. This includes excavating the damaged asphalt and sub-base, improving subgrade support (potentially with geotextiles for stabilization), and replacing it with a new, properly compacted asphalt layer. Preventing alligator cracking requires ensuring adequate pavement design thickness, improving drainage, and using high-quality materials.
2. Potholes
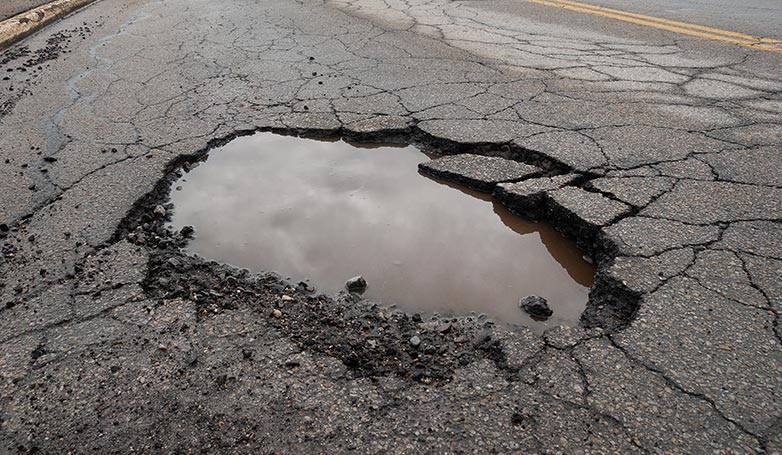

Potholes form when water infiltrates through cracks into the underlying pavement layers, freezes, expands, and then thaws, creating voids. Traffic over these voids causes the surface layer to collapse. They are a result of water damage, poor pavement maintenance, and the freeze-thaw cycle.
How to Solve
To repair potholes, remove debris and water from the hole, apply a tack coat to enhance adhesion, then fill with a high-performance patching material, and compact the patch to level it with the surrounding surface. Long-term solutions include improving drainage, sealing cracks to prevent water infiltration, and applying a pavement overlay to reinforce the surface.
Diving deeper, let’s explore another prevalent problem of asphalt roadways
3. Rutting
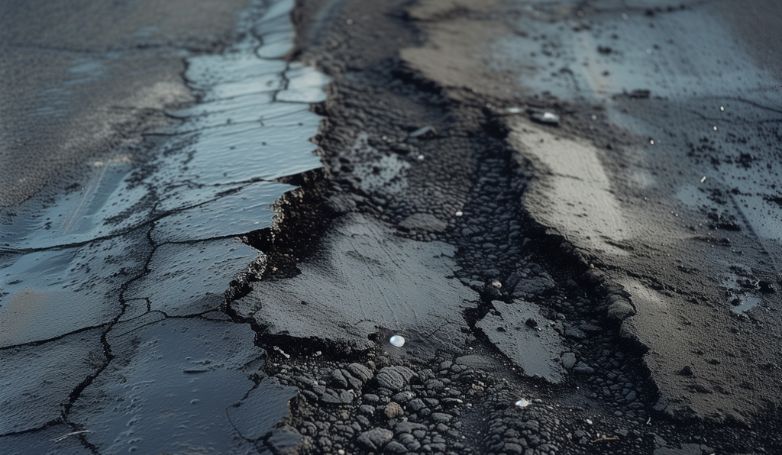

Rutting is caused by deformation or consolidation of pavement layers or subgrade under the repeated pressure of traffic loads. It is often due to inadequate compaction of the pavement layers, poor mix design, or insufficient thickness of the pavement structure.
How to Solve
Repairing rutting may involve milling the affected surface and applying an overlay or, for severe cases, removing and reconstructing the damaged pavement layers. Ensuring proper initial pavement design, using rut-resistant asphalt mixes, and achieving through compaction during construction are crucial to prevent rutting.
4. Fatigue cracking
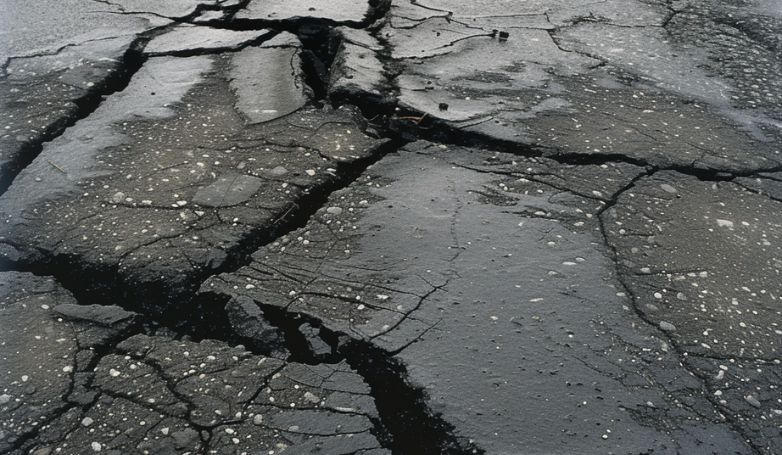

Fatigue cracking is primarily caused by the asphalt pavement’s deterioration under the stress of repetitive loading, beyond what it was designed to withstand. Factors contributing to this include inadequate pavement thickness, poor construction practices, and aging of the asphalt material. Over time, these cracks can evolve into interconnected patterns, resembling the skin of an alligator.
How to Solve
The remedy for fatigue cracking involves removing the damaged pavement layer and addressing any underlying structural issues. This may include reinforcing the base or subgrade to improve its load-bearing capacity. The area should then be filled with a new layer of asphalt mix, properly compacted to ensure durability. Preventive measures, such as selecting a suitable pavement design for the expected load and regular maintenance, are essential to mitigate future occurrences.
Next up, another critical issue among the myriad problems of asphalt roadways.
5. Upheaval
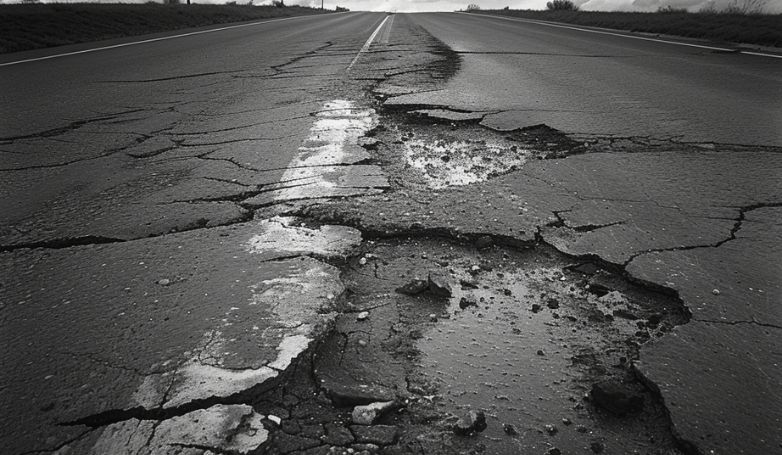

Upheaval in asphalt pavements is typically caused by the expansion of subsoil due to moisture or frost action. This problem is most prevalent in areas where water can infiltrate the pavement layers and then freeze, expanding and pushing the pavement upward. Poor drainage and the presence of expansive clays in the subgrade can exacerbate this issue.
How to Solve
Correcting upheaval involves removing the affected section of pavement, correcting the moisture or frost issues, and then replacing the pavement. This may include improving drainage around the area, using water-resistant materials, and ensuring the subgrade is properly compacted and stabilized. A geotextile fabric barrier may also be used to separate the subgrade from the base material, preventing moisture migration.
6. Reflection cracking
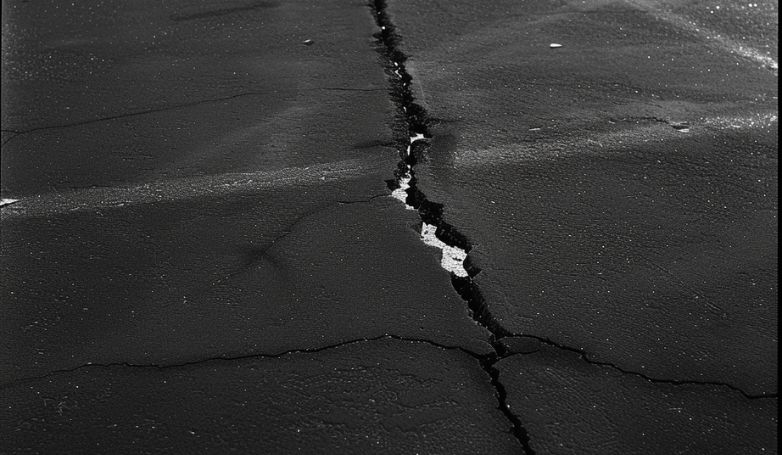

Reflection cracking occurs when cracks in the underlying pavement layer or concrete slab propagate into the asphalt overlay. These cracks are caused by the movement and shifting of the pavement below, often due to temperature changes, moisture, and traffic loads. Inadequate bonding between the overlay and the existing pavement can also contribute to reflection cracking.
How to Solve
To address reflection cracking, a crack-relief layer or interlayer system can be used between the old pavement and the new overlay to absorb stresses and prevent cracks from reflecting upward. Applying a stress-absorbing membrane or using a highly flexible asphalt mix for the overlay can also help. Proper surface preparation and ensuring a good bond between the layers are crucial steps in preventing reflection cracks.
7. Edge cracking
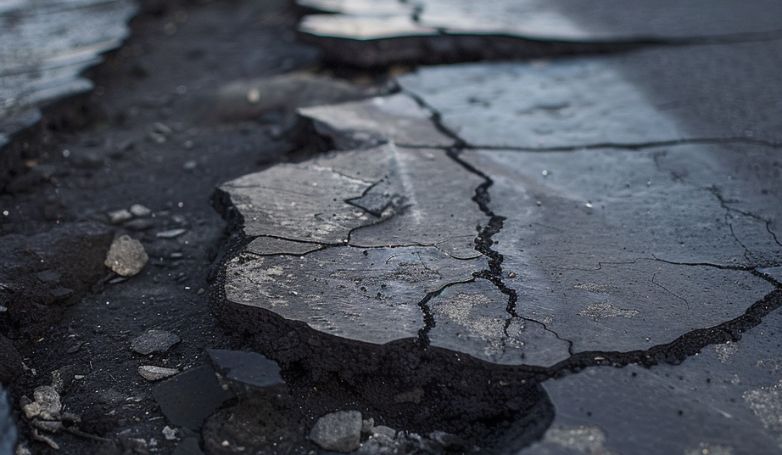

Edge cracking appears along the pavement edges, typically caused by weak edge support, heavy traffic loads, and lack of lateral support. These cracks can also result from poor drainage, leading to water accumulation and weakening of the pavement structure at the edges.
How to Solve
Repairing edge cracking involves sealing the cracks to prevent water infiltration and adding additional support along the pavement edges. This can include widening the pavement or improving the shoulder area with better materials to provide stronger support. Enhancing drainage along the edges to prevent water accumulation and ensuring the pavement has adequate thickness and compaction near the edges are also effective preventative measures.
Moving on, we uncover yet another significant problem of asphalt roadways.
8. Cracking
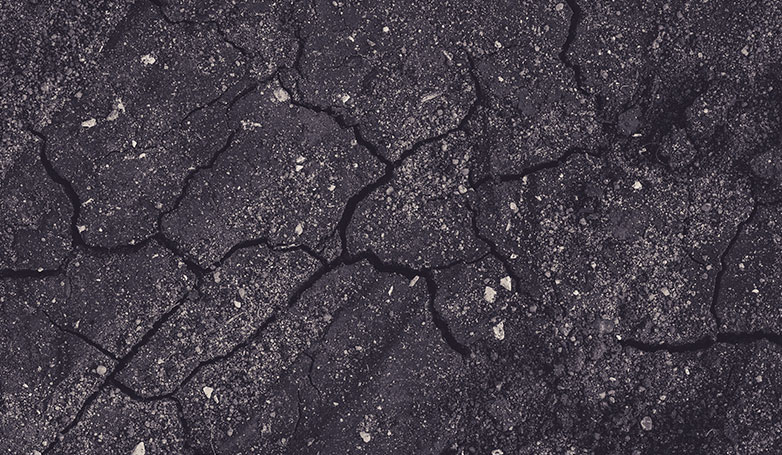

Cracking in asphalt surfaces can result from various factors, including thermal expansion and contraction, moisture infiltration, oxidation from sun exposure, and the underlying base’s movement or settling. Cracks can be further categorized by their patterns, such as longitudinal, transverse, and block cracking, each indicative of specific underlying issues.
How to Solve
Addressing cracking involves first determining the crack type to apply the correct repair method. For surface-level cracks, crack sealing is an effective solution, using rubberized asphalt compounds that flex with the pavement’s movements. For more severe cracking, a full-depth patch may be necessary, removing and replacing the affected pavement area. Preventive measures include proper pavement design, using materials resistant to temperature and moisture changes, and regular maintenance to address issues early.
9. Depressions

Depressions in asphalt pavements are localized low spots that collect water. They are often caused by insufficient compaction during construction, leading to a settling of the pavement surface, or by the failure of the underlying base or subgrade materials.
How to Solve
Repairing depressions typically involves removing the depressed area of the pavement, correcting any issues with the base or subgrade, such as by ensuring proper compaction or replacing weak materials, and then applying a new layer of asphalt. To prevent depressions, it’s crucial to ensure uniform compaction during the initial pavement installation and to address any drainage issues that could exacerbate settling.
10. Patch failures
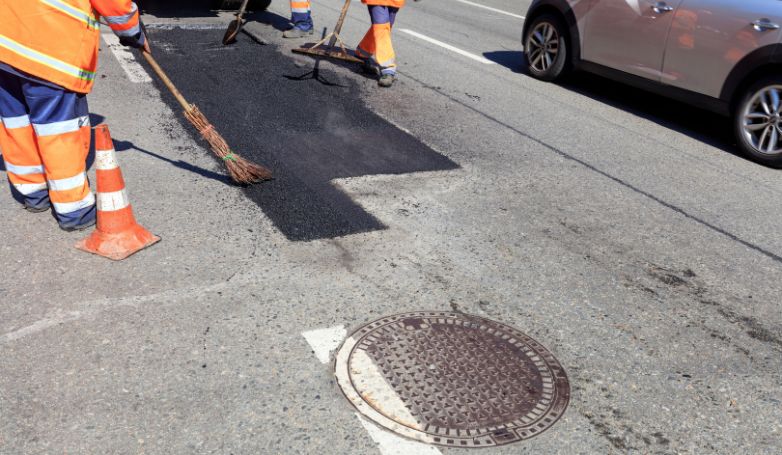

Patch failures often occur due to poor adhesion between the patch material and the existing pavement, inadequate compaction of the patch, or the use of low-quality patching materials. Moisture infiltration and the presence of debris at the time of application can also lead to premature failure of the patch.
How to Solve
To effectively repair patch failures, it’s essential to remove any loose or failed material completely, clean the area thoroughly to ensure good adhesion, and apply a tack coat if necessary. Using high-quality, durable patching materials and ensuring proper compaction will help ensure the longevity of the repair. Regular monitoring and maintenance of patched areas can also prevent future failures.
Let’s not overlook this lesser-known problem of asphalt roadways.
11. Shoving
Shoving is a form of pavement distortion where the surface appears to have been pushed forward, creating ripples or bulges. This issue is typically caused by stopping or turning vehicles in hot weather, which can soften the asphalt, or by a weak or unstable base or subgrade. Poor aggregate gradation in the asphalt mix can also contribute to shoving.
How to Solve
Correcting shoving may involve milling the affected area and replacing it with a new, more stable asphalt mix, ensuring proper aggregate gradation to resist deformation. Strengthening the underlying base or subgrade can also help prevent future shoving by providing a more stable support structure. Employing designs that accommodate or distribute loads more effectively, such as thicker pavement sections or improved material selection, can mitigate shoving issues.
12. Corrugation and shoving
Corrugation and shoving occur when the asphalt surface develops waves or ripples due to traffic loading, especially in areas of acceleration or deceleration. These issues can be attributed to a weak or unstable base, insufficient pavement thickness, poor mix design, or excessive asphalt temperature during application.
How to Solve
The solution involves removing the affected pavement area and correcting the underlying cause, such as stabilizing the base or subgrade, improving the mix design to ensure proper aggregate interlock and asphalt binder stiffness, and ensuring the new pavement layer is properly compacted. Using asphalt mixes designed for high-stress areas can also prevent corrugation and shoving.
13. Raveling
Raveling is the loss of aggregate from the asphalt surface, leading to a rough and pitted appearance. It is often caused by a weak asphalt binder, poor aggregate quality, inadequate compaction, or aging of the pavement.
How to Solve
To repair raveled areas, it may be necessary to apply a thin overlay or surface treatment that reintroduces asphalt binder into the pavement. Ensuring the use of high-quality paving materials, proper compaction techniques, and protecting the pavement from water damage can help prevent raveling. Regular maintenance and sealcoating can also extend the pavement’s life by protecting the surface from the elements.
Now, let’s shift our focus to a more insidious problem of asphalt roadways.
14. Bleeding

Bleeding occurs when asphalt binder accumulates on the pavement surface, creating a slick, shiny surface. This issue is often the result of too much asphalt binder in the mix, inadequate aggregate absorption, or high temperatures softening the asphalt.
How to Solve
Addressing bleeding may involve applying a layer of sand or fine aggregate to absorb excess binder and restore surface texture. In severe cases, milling the affected surface and applying a new wearing course with a corrected mix design may be necessary. Adjusting future mix designs to ensure a proper balance between asphalt binder and aggregate can prevent bleeding.
15. Polished aggregate

Polished aggregate results from the wearing down of pavement surface aggregates, leading to a smooth and slippery surface. This condition is typically observed in areas with high traffic volumes, where the repeated action of tires polishes the aggregate.
How to Solve
Restoring surface texture can involve applying a surface treatment, such as slurry seal or microsurfacing, which adds new aggregate to the pavement surface. Selecting aggregates with higher resistance to polishing for use in asphalt mixes can also prevent this issue in new pavements. Implementing traffic calming measures to reduce vehicle speeds can decrease the rate of aggregate polishing.
Highlighting another challenge, we delve into a common problem of asphalt roadways.
16. Oil
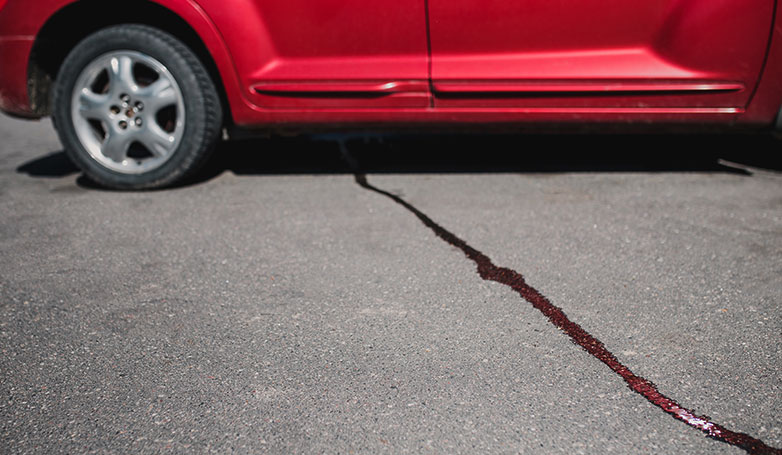

Oil spots on asphalt pavements are usually due to vehicle leaks, which soften and degrade the asphalt binder, leading to pavement deterioration; these oil-induced pavement issues not only compromise structural integrity but also pose environmental risks as the leaked substances can contaminate surrounding soil and water.
How to Solve
Cleaning oil spills promptly can minimize damage. For small affected areas, removing the contaminated asphalt and patching with new material may be sufficient. For larger spills, specialized cleaning agents designed to break down oils before patching can be effective. Preventive measures include regular pavement cleaning and applying sealcoating to protect the asphalt surface from oil penetration.
Conclusion
In conclusion, maintaining asphalt pavements requires vigilance and an understanding of the various types of distresses they can experience, from fatigue cracking to oil contamination. Each problem, from the structural issues like corrugation and shoving, to surface degradation such as raveling and polished aggregate, has its specific causes and remediation strategies. By addressing the underlying causes, employing the right repair techniques, and taking preventive measures, the lifespan and performance of asphalt pavements can be significantly improved. Regular monitoring and maintenance, coupled with the use of quality materials and construction practices, are key to preventing pavement deterioration and ensuring safe, durable roads for the future.


